
Ultimate Guide to Education Degrees
The COVID-19 pandemic brought a sense of urgency to what we view as an essential occupation. As kitchen tables became desks and the weight of the classroom shifted from the schoolhouse to the home, the value of teachers in educational and civic life was more evident than ever.
Teachers don’t get into the education business for the money. However, this career path does provide stability and a consistent level of growth that allows for:
- Career advancement
- Increased pay
- Incentivized educational opportunities
- Access to leadership roles
According to the Bureau of Labor Statistics, education careers from kindergarten teachers to high school principals show a projected 7% growth over the next decade. As exiting teachers and educators retire, more positions will become available, too.
The following guide explores the various levels of education degrees, what you can expect from these programs, and what these degrees can do for your career. We also highlight academic concentrations, detail standout academic programs, and review a list of scholarship opportunities. Continue reading to learn more about education degrees and how you can begin your academic journey toward a career in this essential field.
Types Of Education Degrees
From associate degrees to doctoral programs, education degrees exist for students with varying levels of academic and professional experience. The following section examines the different educational options, what each degree involves, and what you can expect as a student. Additionally, we spotlight several standout academic programs.
Education Certificate Program
Education certificate programs offer bachelor’s-holding teachers a pathway to academic specializations and career advancement without having to earn a graduate-level degree. An especially appealing option for individuals without the time or money to attend graduate school, education certificate programs can introduce new teaching content areas or prepare teachers to work with different grade levels.
Keep in mind, education certificate programs are designed for licensed teachers or recent education grads who plan on earning their teaching license. Education certificate programs are not a pathway to teacher licensure. Various teaching certificates exist, including the following:
- Adult Education
- Administration and Leadership
- Early Childhood Education
- Educational Technology
- English as a Second Language
- Gifted and Talented Education
- Special Education
Teachers interested in pursuing a career-advancing educational certificate must have a bachelor’s degree, and many programs require a minimum cumulative GPA of around 3.0. Additionally, some programs may require you to submit proof of teacher licensure.
Education Certificate Program Spotlight
Associate Degree in Education
An online associate degree—and associate degrees, generally—offer students a unique opportunity to knock out general education requirements and seamlessly transition into four-year programs. Additionally, many associate degrees in education provide paraeducator career training and a pathway to pre-K licensure.
Associate degrees are often part of a 2+2 program where students complete their first two years at a community college and then transfer to a four-year institution to finish their bachelor’s degree. Throughout their associate degree, students tackle general education requirements like English composition and U.S. history while engaging with concentration areas like special education, early childhood education, and secondary education.
AA vs AS in Education: Which Degree Should You Get?
Associate degrees traditionally come in two forms: an associate of arts (AA) or an associate of science (AS). AA degrees typically focus more on the humanities, with students taking more electives in areas like history, English, and foreign language studies. AS degrees tend towards math and science. For students interested in teaching in STEM areas, earning an AS degree is a practical academic option.
Education Associate Program Spotlight
Bachelor’s Degree in Education
Earning a bachelor’s degree in education is often the first step toward beginning your teaching career. A typical major offered by colleges and universities across the country, a bachelor’s in education traditionally requires students to complete 120 credits of coursework and takes most students at least four years to complete.
In addition to general education and core education requirements, many education programs allow students to focus on a chosen subject, age, or student population. Common areas of academic concentration include:
- Elementary education
- Secondary education
- STEM
- Special education
- Early childhood education
Students earning an online bachelor’s in education can complete the vast majority of coursework online and at their own pace. That said, education programs do require extensive hands-on learning through various student teaching and internship experiences.
BA vs BS in Education: Which Degree Should You Get?
Each college or university largely determines whether a bachelor’s in education is identified as a bachelor of arts (BA) or a bachelor of science (BS). These designations do not reflect a program’s rigor and are often influenced by how a particular school catalogs its classes.
That said, a BA degree usually requires a foreign language component, while a BS may involve more math and science coursework. Be sure a program has the appropriate accreditation and leads to teacher licensure.
Bachelor's in Education Program Spotlights
Master’s Degree in Education
The desire to earn a master’s degree in education often stems from two practical reasons:
- A working teacher wants to enhance their skills and expand career options, or
- An individual has a bachelor’s degree and wants to begin their career in teaching
Either way, these degrees explore the most cutting-edge research in the education field and prep graduates for various administrative and leadership roles.
Like many master’s programs, this advanced education degree typically requires students to complete 30+ credits of coursework. Full-time master’s students can complete these programs in 1-2 years. Standard master’s-level classes include research in education, planning for school improvement, teacher leadership, and instructional strategies and models. Before graduation, these programs require a degree-culminating experience in the form of a thesis, research project, or professional portfolio.
While admission requirements vary between programs, students are expected to hold a bachelor’s degree from a regionally accredited college or university. Other standard requirements include a minimum 3.0 GPA, letters of recommendation, and a valid teaching license.
MEd vs MAT: Which Degree Should You Get?
Once you’ve decided to earn a Master’s in Education, there are two distinct academic tracks: master of arts in teaching (MAT) or master of education (MEd). An MAT degree primarily focuses on teaching and highlights topics like pedagogical theory, instructional strategies, and student teaching. An MAT is the degree of choice for career-changers who want to begin their teaching career—many programs offer a pathway to teacher licensure.
Alternately, an MEd degree is primarily for experienced educators and focuses on educational administration, student counseling, and curricular design. To gain admission, the programs typically require at least two years of teaching experience.
Master's in Education Program Spotlights
Doctoral Degree (EdD) or PhD
A doctorate in education is the premier degree for education professionals. In addition to opening up post-secondary teaching opportunities, this high-level degree often qualifies graduates for administration roles like a school principal or superintendent.
Whether online or on-campus, these doctoral degrees usually require that students complete 45-60 credits before graduation. Degree-seekers with a master’s degree can often complete their doctorate in approximately three years. In addition to core requirements, doctoral candidates choose from common academic specializations such as:
- Instructional design
- Special education
- Early childhood education
- Diversity and equity in education
Prospective students are traditionally expected to have experience in the classroom or with educational administration. Applicants should expect to submit a professional resume, academic transcripts, letters of recommendation, and a statement of purpose outlining academic and career goals.
EdD vs PhD: Which Degree Should You Get?
While earning a Doctorate in Education can expand career options and earning potential, these degrees lead to distinct roles. A PhD in Education is research-heavy and leads to careers in academia and various research settings. On the other hand, an EdD degree is a common choice for individuals seeking leadership roles in education, focusing on the practical application of educational theory and research.
Doctorate in Education Program Spotlights
Education Program Areas and Specializations
Education degrees cover a vast array of topics, grade levels, and career outcomes. Because of this, most programs include specializations to help students focus their knowledge and training in a specific area that leads to their intended career.
In the following section, we look at a few of these specializations. This does not constitute an exhaustive list, so make sure you research several schools to find one with a specialization that aligns with your interests.
What Can I Do With An Education Degree?
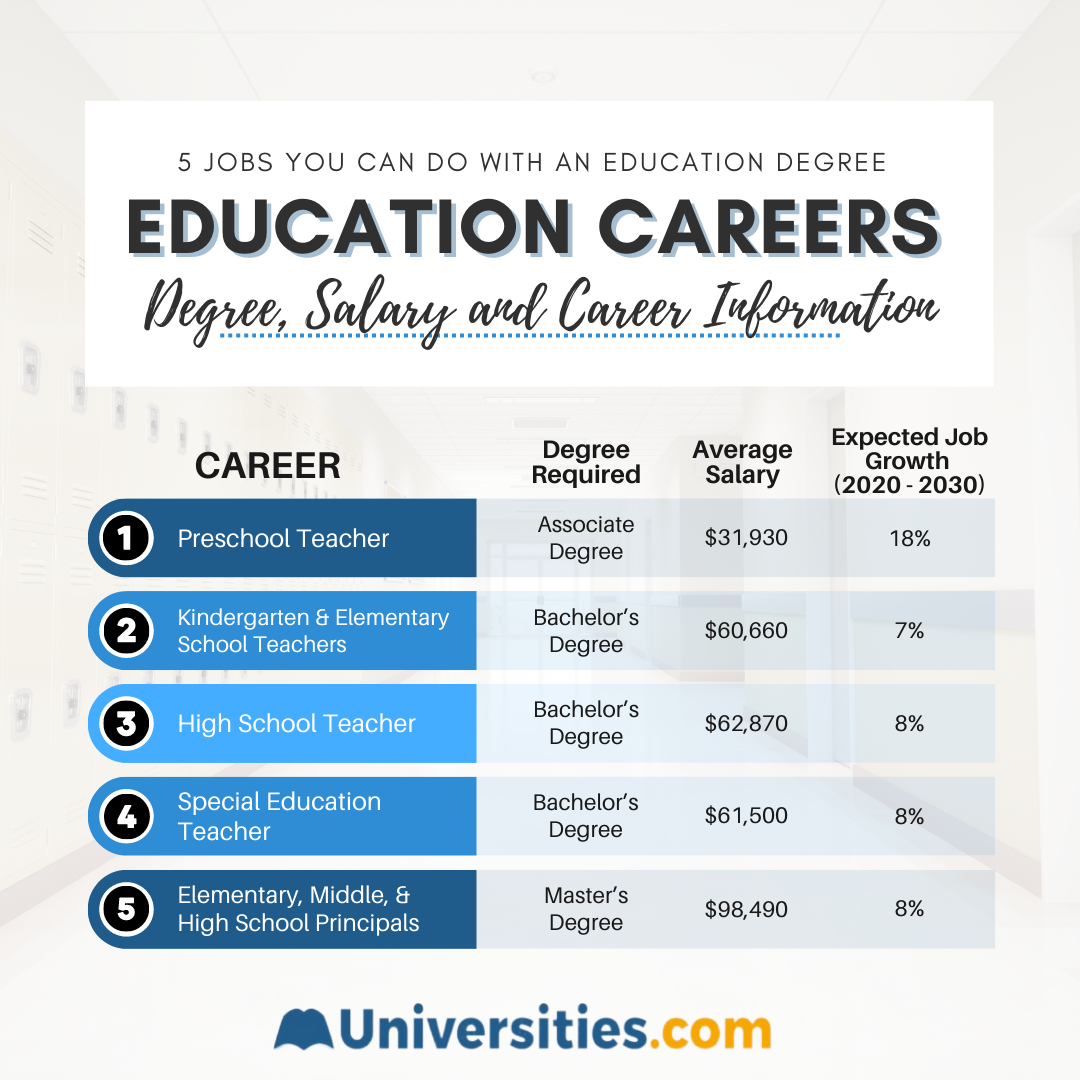
While various factors determine the annual salary for teachers, one statistic remains constant for teachers nationwide: from kindergarten teachers to high school principals, the Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS) projects that the job market for educators should expand between 2020-2030. Salaries can fluctuate significantly depending on an area’s cost of living, and as a general rule, educators with a master’s degree tend to make more.
We’ve highlighted various teaching careers below and included their average salary, projected job growth, and the level of education required.
Education Career Salaries, Career Outlook, and Job Requirements
| Career | Salary | Project Job Growth (2020-2030) | Education/Experience Required |
| Preschool Teacher | $31,930 | 18% | Associate Degree |
| Kindergarten and Elementary School Teachers | $60,660 | 7% | Bachelor’s Degree |
| High School Teacher | $62,870 | 8% | Bachelor’s Degree |
| Special Education Teacher | $61,500 | 8% | Bachelor’s Degree |
| Elementary, Middle, and High School Principals | $98,490 | 8% | Master’s Degree |
How To Become A Teacher: Education and Teaching Licensure
1. Earn Your Bachelor’s Degree
Whether or not you earn a bachelor’s in education, you’ll need a bachelor’s degree to teach in almost any primary or secondary educational setting. Students earning a bachelor’s in education have a clear path towards teaching licensure.
Students with an undergraduate degree in an unrelated field can supplement their bachelor’s with a master’s degree in teaching. Many of these programs offer a pathway towards a teaching license. Teacher preparation tracks do exist, but if you’re already taking the time to complete college-level coursework, earning a master’s degree can also lead to a higher salary and expanded career options.
2. Teaching Licensure
Once you’ve completed your requisite college-level coursework, the next vital step is securing your teaching license. While private schools are traditionally free to set their own hiring guidelines, public teachers jobs require applicants to have an active teachers license.
Education students at a state-approved program often complete many licensure requirements as part of their degree. Students either complete the national Praxis exam or complete a state-specific examination.
For state-specific licensure requirements, the U.S. Department of Education offers a handy resource where you can access contact information for each state.
Teaching Degree Accreditation
While students have access to thousands of colleges and universities throughout the United States, not all schools and academic programs are created equally. When searching for the right education degree program, enrolling in a regionally accredited institution is essential. Regionally accredited schools have met rigorous standards to ensure that you get your money’s worth. Accreditation can also influence your ability to receive Federal financial aid and whether or not the credits you earn can be transferred to other institutions.
It’s also vital that your education program holds programmatic accreditation. This is especially important if you are working towards teacher licensure. The National Council for Accreditation of Teacher Education (NCATE) is a common accrediting agency for education programs.
The U.S. Department of Education’s Office of Postsecondary Education offers a valuable database of accredited institutions and programs.
Scholarships For Education Students
A vast number of scholarships are available for education students. And whether you’re tackling your bachelor’s degree or MEd, funding exists. Additionally, many states offer tuition reimbursements for students dedicated to working in a particular state. We’ve highlighted five generous scholarships below. For a more extensive and personalized list of scholarships, visit our scholarship search tool.
Indiana Retired Teachers Foundation Scholarship: Awarded to full-time college sophomores and juniors at Indiana colleges or universities, the Indiana Retired Teachers Association provides scholarships exceeding $2,000. Applicants must submit academic transcripts, letters of recommendation, and documentation of financial need.
Minority Teacher Education Scholarship Program: Sponsored by the Florida Fund for Minority Teachers, this scholarship initiative offers a merit-based program providing funding exceeding $4,000. Applicants submit an electronic application and a short essay.
Next Generation Hoosier Educators Scholarship: For students planning to teach in Indiana schools after graduation, this scholarship awards over $7,500 in funding. Applicants must graduate in the top 20% of their high school class or have a top 20% SAT/ACT score.
PNC Foundation Scholarship: In partnership with the United Negro College Fund (UNCF), this scholarship program was founded to expand educational access to minority students in New Jersey. Students must enroll in an education program and submit a completed application, academic transcripts, and a personal essay.
Winifred R. Reynolds Educational Scholarship: Offering winners up to $7,000, this scholarship is open to students pursuing graduate degrees focusing on early childhood education, childhood development, or an equivalent field.
Frequently Asked Education Degree Questions
Check out our newsletter to stay updated on college updates, news, advice, and more.
